Blog Details
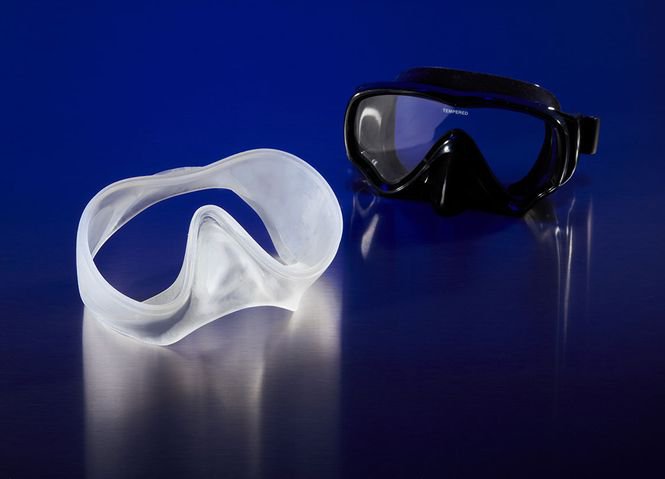

Photo-polymers for 3D Printing/ Additive Manufacturing
Posted on
#Vat photopolymerization (SLA,DLP) #All applications #Aerospace #Mechanical #Fashion #Architecture #Medical device #Health industry #All materials #Polymers #Composites
Photopolymers are used in two different additive manufacturing (AM) processes; Vat photopolymerization AM (commercial names: SLA, CLIP, DLP, Multiphoton lithography), Material jetting AM (also known as Inkjet printing, Aerosol jet printing). 3D printing process of above two methods is based on the photopolymerization, which means that the photopolymers undergo chemical reaction to become solid when they are exposed to ultraviolet range of radiation.
In this blog, let us focus on photo-polymers for stereolithography (SLA) 3D printers.
Applications of 3D printed parts with photo-polymer resins
The parts printed with photopolymers offers high dimensional accuracy
and surface quality when compare to quality of parts made using other AM
processes. Such advantages with these materials and AM technology benefiting the
dentistry, fashion, and jewelry industries for making prototypes and functional
parts. Also, mechanical industries employ SLA 3D printers for making concept
models, rapid prototypes, cast urethane/vacuum casting master patterns,
investment casting patterns, jigs and fixtures, snap-fit assemblies, and
form-and-fit testing and other functional parts subject to only static loads.
The SLA printed parts can fulfill application needs for transparency,
high-temperature, high stiffness or other qualities and functions.
Also, bio-compatible photo-polymer resins
developed for health and medical industrial applications that includes surgical
tools/guides, dental appliances, and hearing aids. In last couple of years,
dental industries have been extensively employing the SLA printing technology
for making surgical guides, retainers, aligners, braces, crowns, and orthodontic
replica models.
Photo-polymers for 3D printing
Photopolymers in resin form are used for SLA printing process and they
are limited since the 3D printing process is based on photopolymerization.
Commercially available photopolymer resin material for 3D printing is a
composite mixture based on acrylates and epoxy. The composite
mixture is used to avoid the shrinkage and curling issue with only acrylates,
and fragility with only epoxy. The
addition of acrylate to epoxy resin is required to rapidly build part strength
and this avoids distortion during fabrication. Furthermore, the acrylates also
reduce the brittleness of epoxy parts. Therefore, it is necessary to use resin
made of both materials to combine advantages of both curing types. Most of
materials require post-curing once printing is done to reach their highest
possible strength and stability.
In most cases the resins available in the market are 3D printers (SLA)
specific. It means that the SLA 3D printers are built with specific
configuration for certain resin compositions for producing quality prints.
Therefore, the resins are recommended to purchase from the 3D printer supplier.
Further, resins are available for industrial application and with different
colors.
Let us now explore commercially available photopolymer resins for vat photopolymerization based additive manufacturing. Here we explore resins available from two leading SLA printer makers; 3D systems for industrial printers, and Formlabs for desktop printers. Also, applications and advantages of the resins from both suppliers are discussed in detail below. 3D printed bottle with flexible(elastomeric) photopolymer using Formlabs 3D printer can be seen in the video.
Image credit: Formlabs