Blog Details
4D Printing of Smart Structures and Their Applications
Posted on
#Material Extrusion (FFF,FDM) #Material Jetting #All applications #Aerospace #Mechanical #Electronics #Fashion #Architecture #All materials #Polymers #Composites #Other Technologies
What is 4D printing?
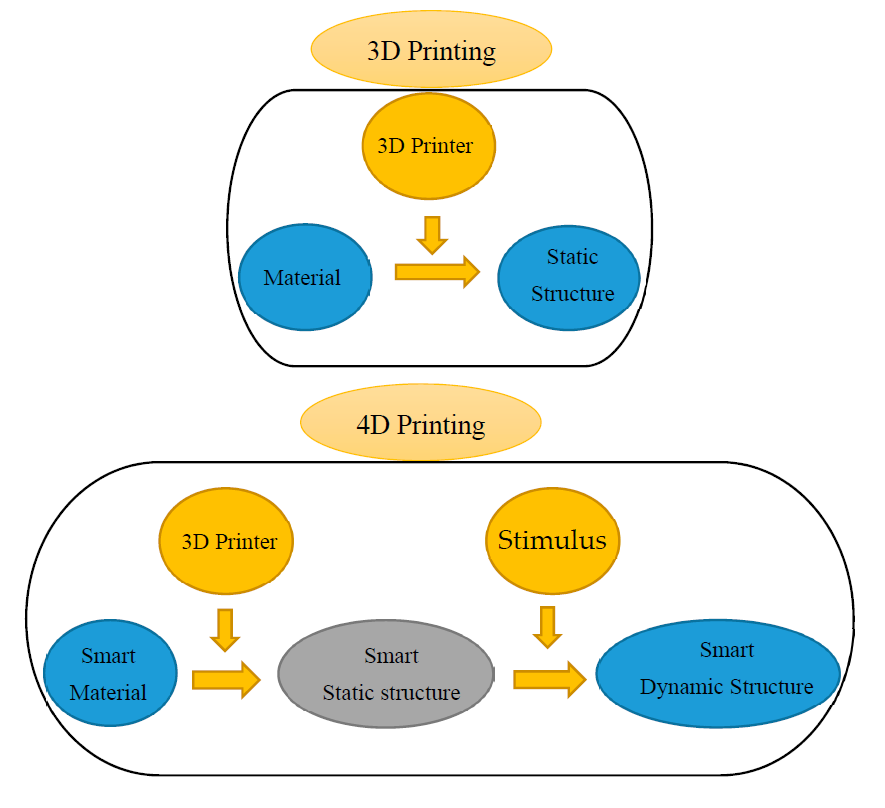
3D printing of parts with smart materials/ responsive materials/programmable materials is called 4D printing. Geometrical shape of such printed parts changes over time (another dimension) when exposed to certain environment (humidity, temperature, electric, magnetic ..), and is mainly because of the response of materials to the environment. Parts made with responsive materials also called smart structures, in other words 4d printing produces smart structures.
4D printing work initially carried-out in 2014 by researchers at Self
Assembly lab, MIT, USA and in collaboration with Stratasys and Autodesk.
Some of their work can be found here.
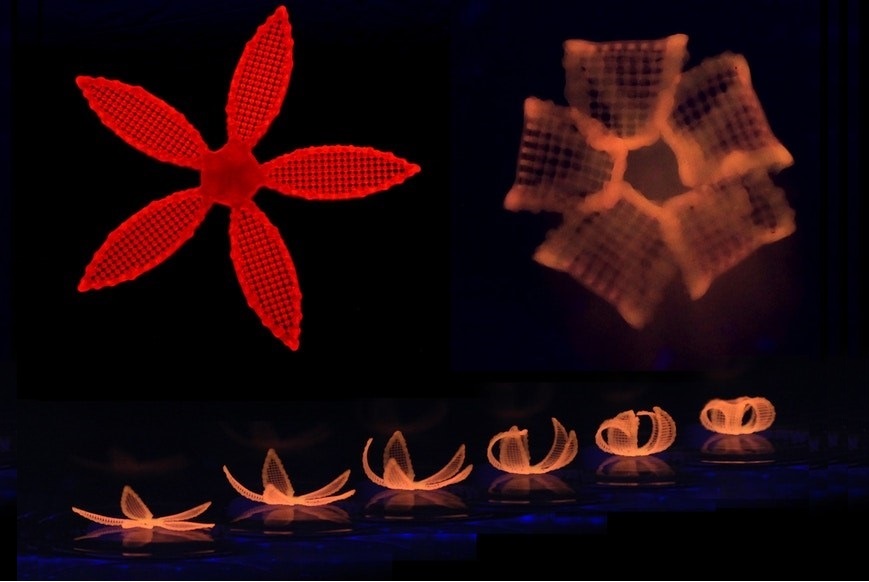
Self-foldable 3d printed structures can be seen in below video- 3D printed structure is transforming its geometrical shape when exposed to water.
Shapeshifting 3d printed architecture: ‘Researchers at the Wyss Institute have mimicked a variety of such dynamic shape changes like those performed by tendrils, leaves, and flowers in response to changes in humidity or temperature with innovative 4D-printed hydrogel composites.’
4D printing versus 3D printing
In general, 3d printed parts are static and are not designed to respond to external stimuli energy. Also, 3d printed parts do not undergo large geometrical shape morphing over time. On the other hand, 4D printed structures are no longer simply static, dead objects; rather, they are programmably active and can transform independently.
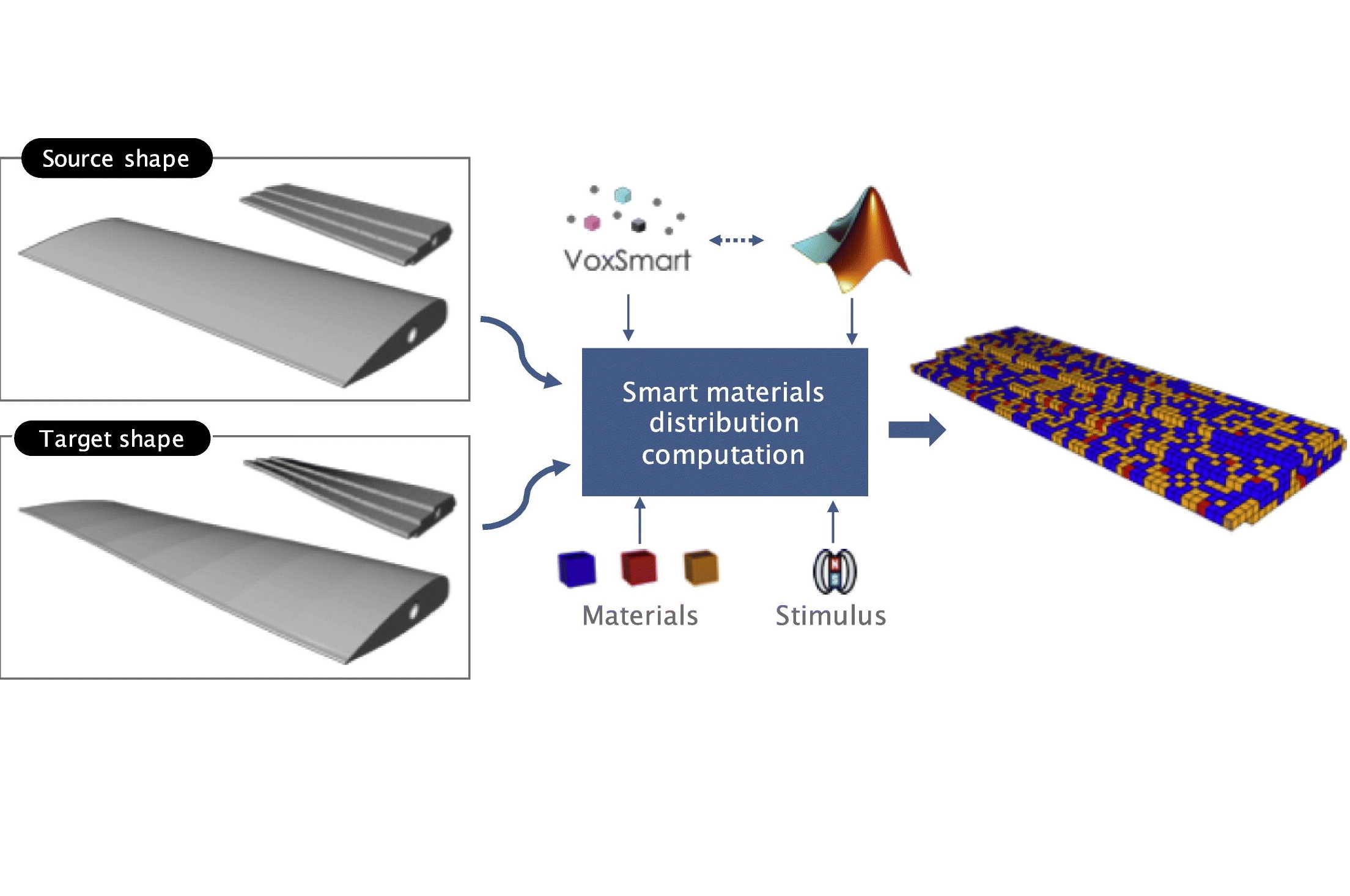
Image credit- Mahdi Bodaghi et al 2019, Materials
Available AM methods and materials for 4D printing of smart structures
- Polyjet method for shape memory polymer and Hydrophilic polymer
- FFF for Hydrogel and Thermochromic materials
- SLA for shape memory polymer and piezo-electric material
- SLM for shape memory alloy
4D printed parts with above materials undergo large strains when they are exposed to heat or moisture or voltage and thereby, causes shape morphing of the printed structures over time.
Applications
So far 4D printed
structures are limited to only prototypes in laboratories, but the technology
is useful for producing structures for adaptability and dynamic response when
are exposed to heat, light or other energy input. Some of applications include smart
textiles, soft electronics, medical devices, and tissue engineering,
self-foldable furniture.